MLsys Note (1) - FlashInfer Cascade Attention & KV Cache Layout

FlashInfer
FlashInfer 是一個集合各種 LLM inference kernel 的 library。提供了 attention, GEMM 和 MOE 的 API。也支援多種 nvidia gpu 架構:turing, ampere, hopper, blackwell。提供多種底層的高效 kernel 實現。
FlashInfer 提出有趣的兩個優化:Cascade Attention 和多種KV-Cache Layout。在許多 inference 場景下,多條 request 是可以被共用的,若是可以共用,即大大減少 KV Cache 存儲,可以在計算上獲得許多收益。一樣,這篇會看算法以及實作層面,若有錯誤,不吝賜教。
Cascade Attention
Flash Attention 1 利用 online softmax 的技巧,大大減少計算 attention 的 in-memory O(n^2) -> O(n)。FA2&3 在 kernel 上進行更合理的優化(tiling)。而 FlashInfer 基於此之上針對 GQA(Group Query Attention) 提出了 attention state 和 merge operator on the attention states。
Attention State
Naive Attention:
Suppose is the pre-softmax attention score between query and the key at index :
we can generalize the definition from single index to an index set:
value vector :
則是整個 sequence 的 self-attention output。The attention state of the index set can be defined as a tuple:
Merge operator
定義兩個 state 的 merge :
對於任何長度的 attention state inputs:
可以注意到這個 operator 是 communicative 和 associative 的,也就是說,對於任何長度的 attention sequence,可以以任何長度切割並合併計算,就是具有 devide & conquer 的性質。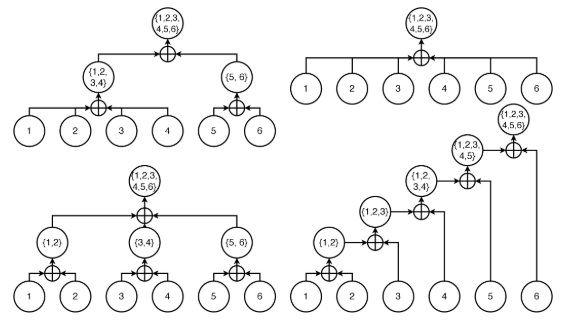
Code:
1 | |
Applications
merge是commutative and associative的,所以我們可以把不同subset of KV offload到不同的device上之後再merge起來。這在許多long-context的設定上有許多好處。
Cascade Inference: Shared-Prefix Batch Decoding
Workflow:
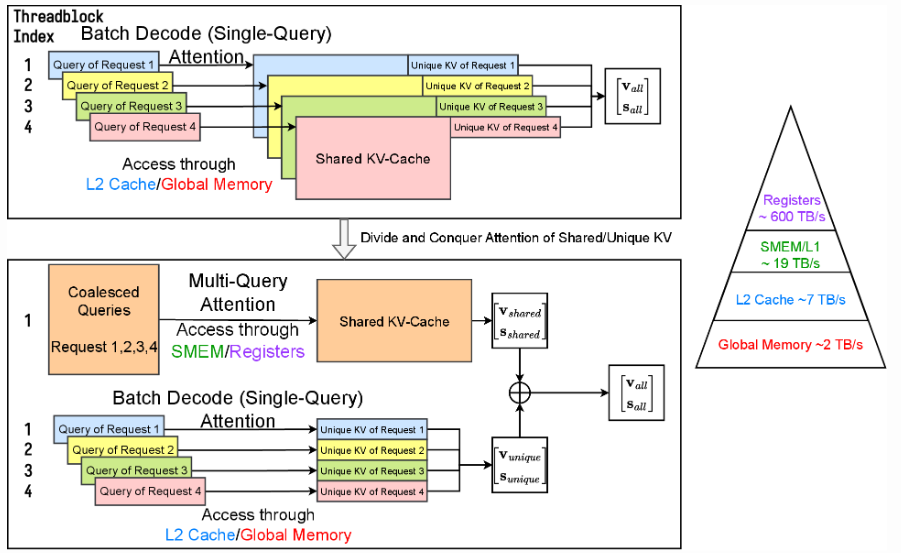
- Use multi-query (prefill/append) attention kernel to compute the attention state between queries and KV-Cache of shared prefix.
- Use batch decode attention kernel to compute the attention state between queries and KV-Cache of unique suffixes.
- Use merge operator to combine two attention states to get the final attention output.

上格是naive作法,對於多個request是獨立處理的,並把KV Cache存在L2 Cache/Global Memory,相對低效。若把前綴相同的部分share起來,shared KV Cache存在SMEM/Registers,在移動shared KV Cache上可以memory efficient。最高可以達到30x的效率收益。
KV Cache Layout
Flasshinfer在vLLM的Page Attention基礎上更進一步優化KV Cache。首先先了解什麽是Paged KV Cache:
Page Attention
核心思想就是把KV Cache用page的方式管理。在OS中,我們知道不同process之間基本上是互相獨立的,每個process覺得自己在使用獨立的空間,但他們使用的memory其實是分享同一個物理記憶體。同理,每一個LLM request都是獨立的,但是因為長短不一,如果真的每個request都維護一個記憶空間是很浪費GPU RAM的,為了防止記憶體碎片化,我們用一個page table,把邏輯上KV的儲存位置mapping到physical KV memory上面。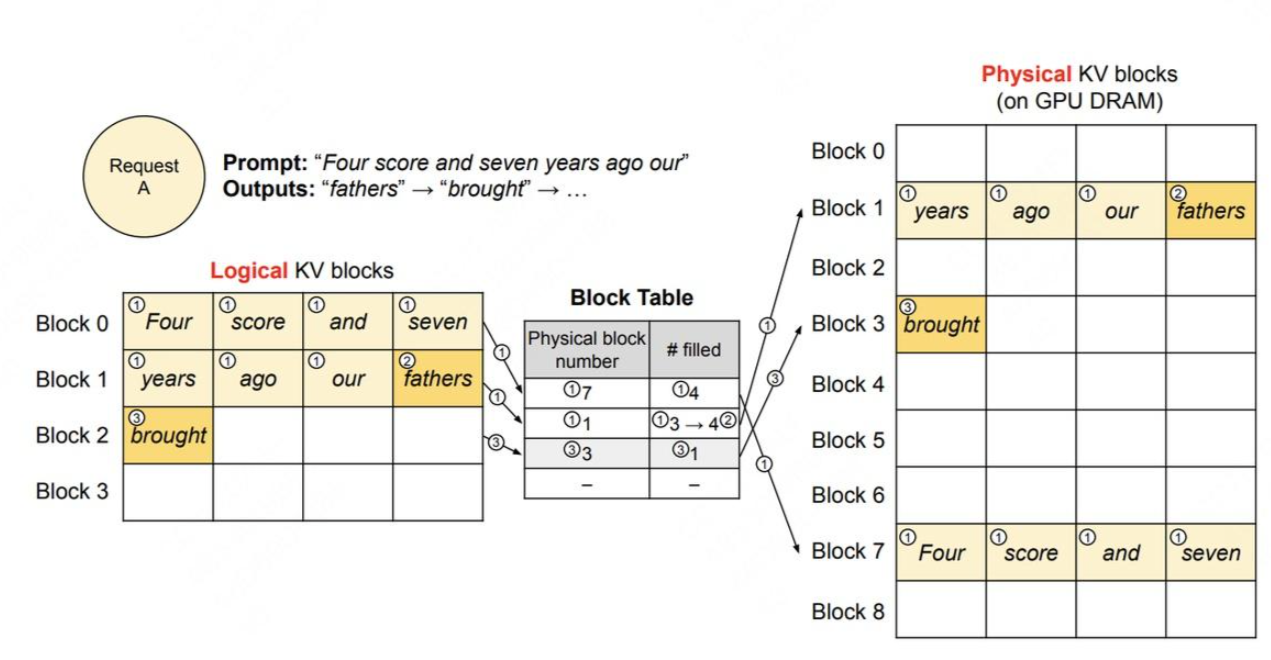
圖中的一個block就是一個page,在vLLM裡一個block可以裝16個token的KV data。
Flashinfer基於此之上,在資料結構層面上做出更急止的優化:
Layout: NHD/HND
KV Cache的最後三個維度,可以分成兩種layout:
1 | |
NHD是最自然的形式,HND在low-precision KV Cache上比較友善,但在fp16時,兩者不會差太多。
Ragged Tensor
在prefill stage會用Ragged Tensor把不同長度的QKV pack成單一個data tensor,省去padding帶來的空間消耗。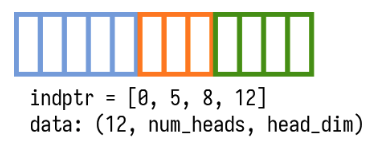
indptr array用來記錄一個data tensor裡不同長度seq的訊息(indptr[i+1]-indptr[i] is the sequence length of request i)。
data tensor size = (indptr[-1], num_heads, head_dim) under NHD.
Page Table Layout
FlashInfer把Paged KV中的Page table當作一個block sparse matrix,並使用CSR Format去index每個page。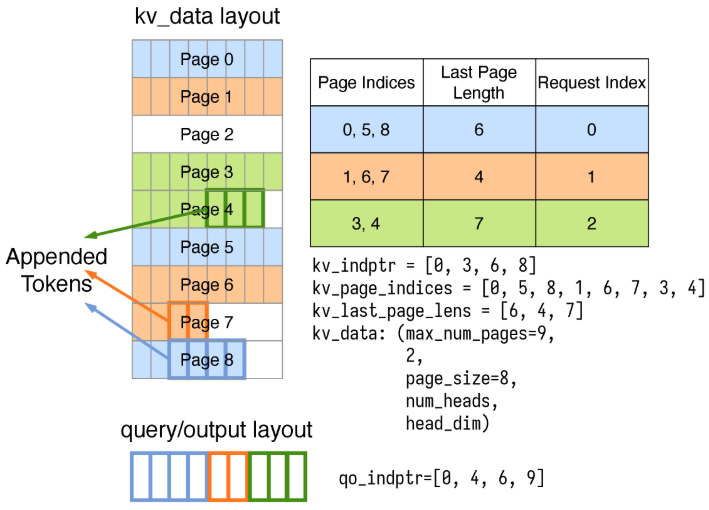
When length = num_requests+1, kv_indptr = [0, len(page_indices[0]), len(page_indices[0])+len(page_indices[1]), …].
1 | |
Multi-level Cascade Inference Data Layout
若把這些layout實際應用在cascade attention上面的話,我們可以做multi-level的prefix reuse: 下圖levels=3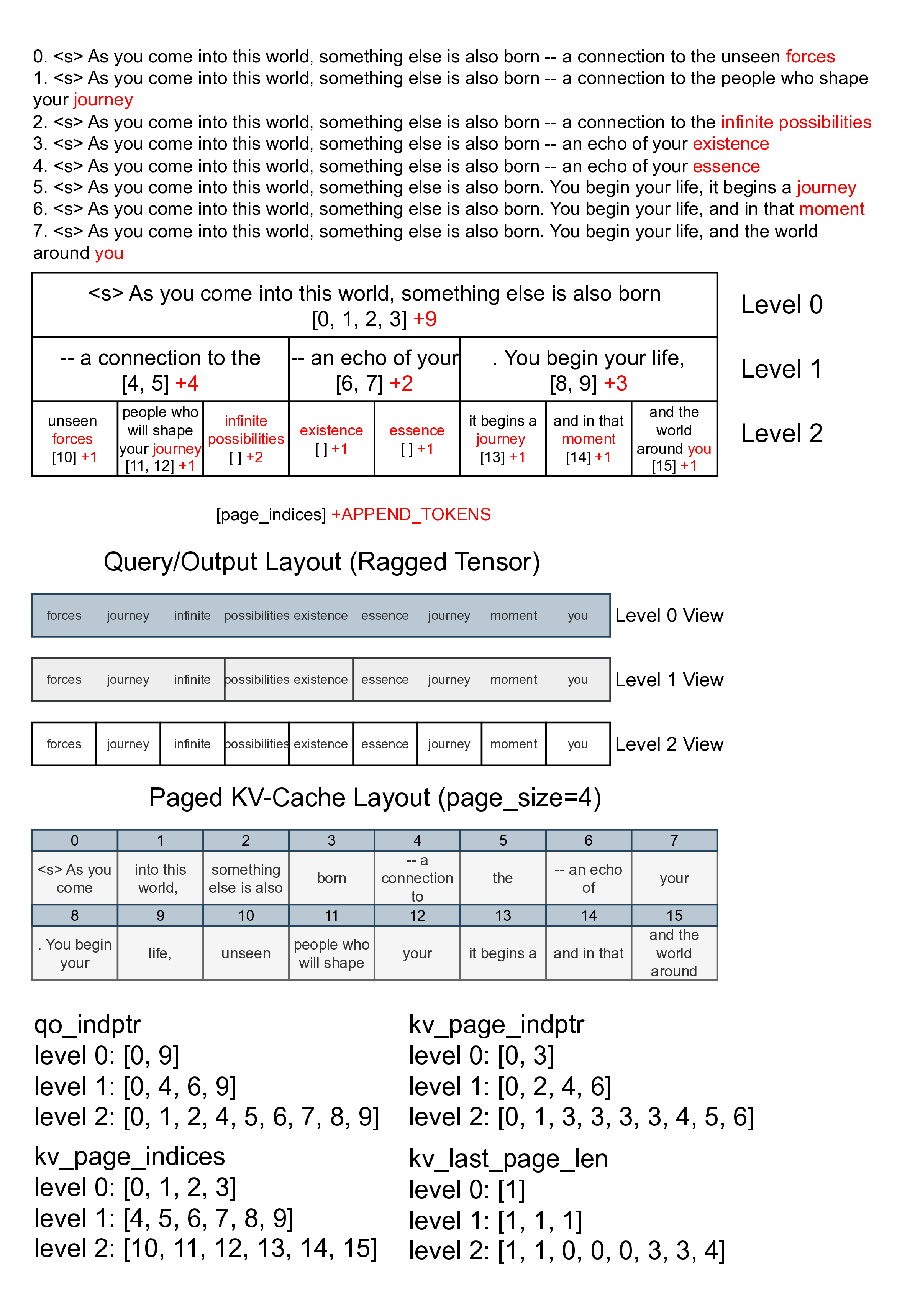
Conclusion
FlashInfer提供了多樣的inference kernel,在attention和kv cache上有良好的效率基礎,利於後序Inference Engine(sglang, vllm)進行開發,接下來我會深入Flash Attention三代的實作與計算,之後就來看LLM Inference Engine是如何schedule request, kv cache達成高效throughtput。